
Uqaab عقاب
A Low SWaP-C positioning system for autonomous drone operations in GNSS degraded and denied environments.
How we make it possible?
Uqaab uses sensor fusion algorithms to combine inertial sensors, pressure sensors, magnetic field sensors, laser range finder and nadir view camera to provide continuous Position, Velocity and Attitude (PVA) solution for autonomous navigation of drones in GNSS denied environments.
A strap down Inertial Navigation System (INS) mechanization using MEMS grade accelerometers and gyroscopes provides high rate PVA solution.
AHRS
Rectified aerial imagery
INS
Aerial imagery from nadir view camera is rectified using AHRS, laser range finder and barometric altitude to correct for roll, pitch, heading and scale variations.
Inertial sensors and magnetic field sensors are used for mechanization of Attitude and Heading Reference System (AHRS) to provide attitude and heading solution for aerial imagery rectification.
GNSS
When Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is available, inertial sensor errors are estimated and corrected using Position, Velocity and Time (PVT) solution available from a GNSS receiver.
VPS
When drone flies in a GNSS degraded or denied environment, the Visual Positioning System (VPS) utilizes rectified aerial imagery to calculate drone's position and velocity vectors, which are used for estimating and correcting inertial sensor errors.
Rectified aerial imagery
Uqaab in action
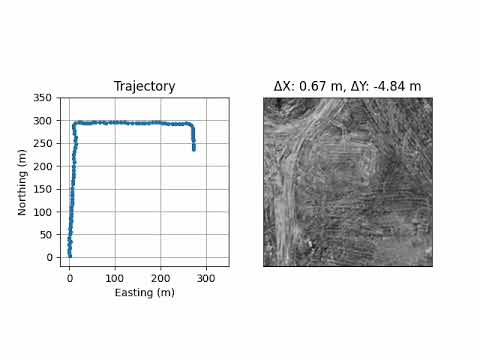
GNSS denied flight over a tactical airfield.
Drone flying at approximately 100 m AGL.
Aerial imagery varies in density of trackable features.
Results show successful position estimation over the airfield.
Drone successfully closed the loop by autonomously flying to the navigation waypoints before returning to the start location.
